Cauliflower - ফুলকপি
Cauliflower (fulkopi in Bengali) is an annual vegetable, grown mainly as Rabi crop during winter, and reproduced by seeds. It's used as fresh or cooked, and sometimes as an ingredient of pickles.

Cauliflower is a cruciferous vegetable, cultivated in winter, from Brassicaceae family that looks like a white version of broccoli. As broccoli, the tightly bunched florets of cauliflower, sometimes called "curd", are connected by a thick core, often with a few light leaves surrounding it. It is an offshoot of a type of wild cabbage similar to kale, Brussels sprouts, and kohlrabi.
While white is the most common color, cauliflowers are found in different shades like orange, purple, and green. Regardless of the color, the taste is the same: slightly sweet, a little nutty, and mild enough to blend well with other dishes with its special crunchy texture.
Cauliflower is cultivated in China, India, United States, and some European countries, but it's originally came from Asia and the Mediterranean region. It arrived and grown in Europe in the late 15th century, but wasn't started growing in US until 19th century. Today, China has the biggest production of Cauliflower (10,707,171 ton/year) in the world, and US comes the third place (1,247,490 tons/year) in its production. Bangladesh, also, produce around 284,327 tons per year which is the eighth biggest production of cauliflower in the world.
Cauliflower in Bangladesh (বাংলাদেশ)
Cauliflower (fulkopi or ফুলকপি in Bengali) is an annual vegetable, grown mainly as Rabi crop during winter, and reproduced by seeds. It's used as fresh or cooked, and sometimes as an ingredient of pickles. In Bangladesh, the production of vegetables, including cauliflower, is increasing day by day. Cauliflower usually dominates a major share of vegetable production in terms of total cropping areas. The acreage of cauliflower cultivation in Bangladesh is around 9,400 hectare and the annual production amounts is about 73,000 million tons. Seedlings of thirty days old are extremely suitable for transplanting in the month of October to November, and yield ranging 25-30 million tons/hectare. Moreover, it grows well in all the districts of Bangladesh, but the majority of cauliflower are produced in Dhaka, Jessore, Rajshahi, Rangpur, Tangail and Kustia.

Cauliflower is grown on various types of soil, but the most suitable is the rich, well drained and irrigated soil with a high moisture-holding capacity. High humus content in the soil will provide better aeration, a process of air circulation in the soil mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or substance, and water penetration. The neutral or slightly acid soil (pH 6.0 to 6.5) is the best for cauliflowers in general; well-drained, sandy loam soils suit the early varieties, and loamy and clay loam soils are best suited for late ones because they somehow tolerate poor drainage. Good soil preparation is crucial during planting the cauliflowers. Find out how it's planted in Bangladesh here.
Three groups of cauliflower are commonly grown in Bangladesh depending on planting time. Early planting or varieties are Kartica, Patnai, Agrahyani, Pusadipali, and early snowball, including Tropical 55 days, Tropical 45 days. Mid-season or medium planting are Agrahani, Poushali, Agrahyani, BARI Fulcopi1 (Rupa), BARI Fulcopi-2, and Snowball X, Y & 16. The late planting are White Mountain, Maghi, and Rakhusi Late. Bangladesh agricultural research institute has released a mid-season high yielding variety named Rupa in 1998.

Health Benefits
- 92 grams out of 100 grams of cauliflower (one serving) are water which means it keeps the consumer hydrated. It is also rich in fiber where one serving contains 2-3 grams of fiber accounting for 10% of the daily needs.
- Cauliflower high in glucosinolates and isothiocyanates, two types of antioxidants that have been shown to slow the growth of cancer cells and protect cells from damage. They also have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antiviral effects.
- Cauliflower contains carotenoid and flavonoid antioxidants which have anti-cancer effects and may reduce the risk of several other illnesses, including heart disease.
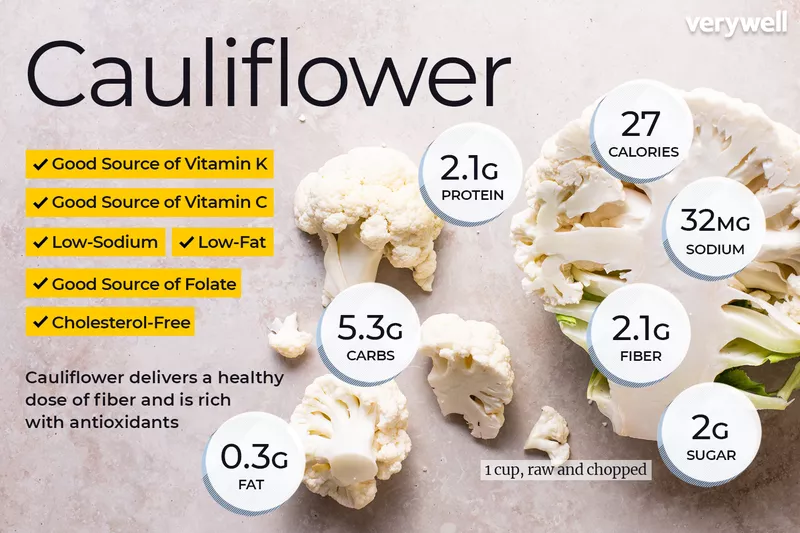
Nutritional Profile
One serving (1 cup =100 grams chopped cauliflower) of raw or cooked cauliflower contains:
Calories: 25-27 calories
Fat: 0-0.3 gram
Carbohydrates: 5 gram
Fiber: 2 gram
Sugar: 2 gram
Protein: 2 gram
Sodium: 30-32 milligram
Magnesium: 16 milligram
Vitamin B6: 0.2 milligram
Vitamin C: 51.6 milligram
Vitamins and nutrients in 1 serving of cauliflower:
- 2% of daily required calcium and iron
- 6% of daily potassium
- More than 3% of daily required magnesium
- Around 1/4 of daily vitamin K
- 100% of the daily recommended amount of vitamin C
How Cauliflower is Consumed Worldwide
Cauliflower is versatile and can be prepared in a number of ways:
- Steamed. The easiest way is to steam it. The whole head or florets can be steamed.
- Roasted. Cut the head of cauliflower into steaks or florets, spread them on a cooking sheet, drizzle with olive oil, and sprinkle with salt and pepper. Roast in the oven until it's golden.
- Pureed. Once cauliflower has been cooked, it can be pureed until it is smooth. It can be as a substitute for cream sauces or add it to smoothies.
- Mashed. Boost the nutrition value of mashed potatoes by steaming some cauliflower and mashing it into them. Or skip the potatoes and opt for low-carb mashed cauliflower instead. You also can mash cauliflower into pizza dough for a lighter crust.
- Grated. Steam cauliflower and then grate it into a rice-like texture.
How Cauliflower is consumed in Bangladesh
- Fried. Cut the cauliflower head into florets, sprinkle with salt, pepper, turmeric, and cumin, and stir-fry for 6 to 8 minutes to get a delicious dish of cauliflower. Chopped onion and garlic are added also for more flavour.
- Cooked. Cauliflower is commonly seen in fish and chicken curry in Bengali dishes. while the curry is boiling, throw few florets into the curry pot until it gets soften.
Adverse Effects
People with certain conditions may need to be cautious and take physician's advice before eating cauliflower.
Thyroid issues. Thyroid is a small gland situated in the neck and it produce important hormones called Triiodothyronine (T3), Tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine or T4), and Calcitonin. For thyroid gland to function properly, it needs iodine. Consuming cauliflower in large amount - let's say the amount of more than what 2 people can eat in one sitting - would keep thyroid from absorbing iodine which will affect the hormones production.
Digestion or GI issues. Cauliflower may cause bloating and gas because it is rich in fiber, especially for people with conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), ulcerative colitis, or Crohn’s disease.
Heart disease. In case taking blood thinners or statins for heart disease, the physician may recommend to avoid foods high in vitamin K because they can affect these medications.
References
Cauliflower, BanglaPedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh.
Cauliflower modern cultivation Process and its health benefits, Agriculture Learning.
Cauliflower Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits, VeryWell Fit.
Cauliflower (Vegetable Crops), Bangladesh Agro-Meteorological Information Portal.
Health Benefits of Cauliflower, WebMid.
Report of productivity survey of cauliflower crop, Bangladesh Bureau and Statistics.
Sharma, S.R.; Singh, P.K.; Chable, V. Tripathi, S.K. (2004). "A review of hybrid cauliflower development". Journal of New Seeds. 6 (2–3): 151. doi:10.1300/J153v06n02_08
The Beginner’s Guide to Cruciferous Vegetables, Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
Thyroid Hormone, Cleveland Clinic.
World Cauliflower and Broccoli Production by Country, Atlas Big.